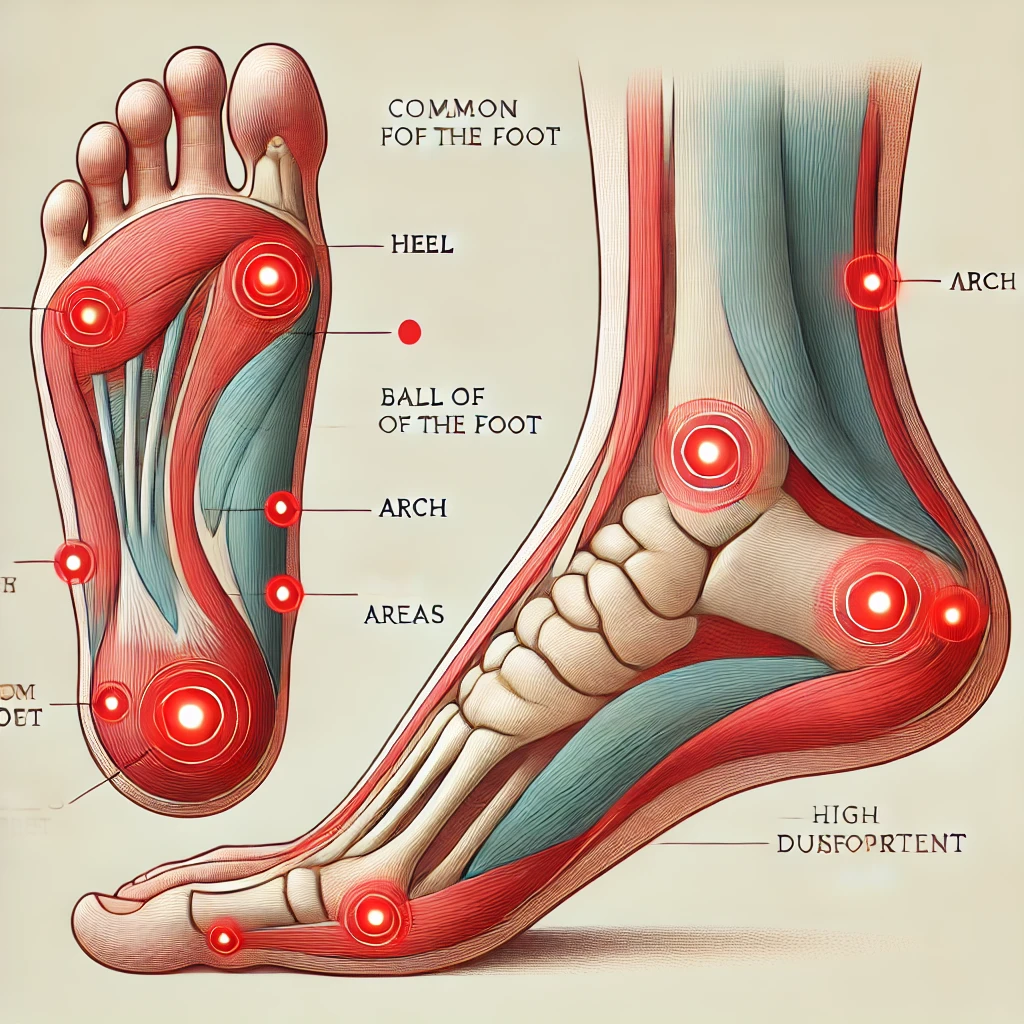
Foot pain can range from mild discomfort to severe, debilitating issues that affect daily life. Understanding the cause of foot pain is crucial in determining the appropriate treatment and prevention methods. One of the most effective tools in diagnosing and addressing foot pain is a foot pain diagram. These diagrams provide a visual breakdown of the foot’s anatomy, showing specific areas where common injuries and conditions occur. In this blog post, we will explore what a foot pain diagram reveals about various injuries and conditions that cause discomfort, helping you better understand your foot health.
1. Understanding the Anatomy of the Foot
Before delving into specific injuries, it’s important to have a basic understanding of the foot’s anatomy. The human foot is an intricate structure comprising 26 bones, 33 joints, and over 100 muscles, tendons, and ligaments. The foot is divided into three sections: the forefoot (toes and ball of the foot), midfoot (arch area), and hindfoot (heel and ankle).
Each part of the foot has unique functions, and problems in any of these areas can lead to pain. A foot pain diagram can help pinpoint which part of the foot is affected and give insight into potential injuries based on the location of the pain.
2. Common Forefoot Injuries: What the Diagram Tells You
The forefoot, including the toes and the ball of the foot, is a common area for injuries. If you’re experiencing pain in this region, a foot pain diagram can help identify potential causes:
-
Bunions: A bunion is a bony bump that forms at the base of the big toe. It often causes pain and swelling, particularly when walking or wearing tight shoes. On a foot pain diagram, bunion pain typically shows up on the inside edge of the foot near the big toe.
-
Morton’s Neuroma: This condition involves a thickening of the tissue around the nerves leading to the toes. It causes sharp, burning pain in the ball of the foot, which may radiate into the toes. A foot pain diagram will usually highlight this pain in the area just behind the toes.
-
Metatarsalgia: This refers to pain in the ball of the foot, often due to overuse, improper footwear, or high-impact activities. A foot pain diagram will show discomfort in the metatarsal region, often exacerbated by standing or walking.
3. Midfoot Injuries: What Does the Diagram Show?
Pain in the midfoot region can be particularly distressing, as this area plays a significant role in providing support and balance. A foot pain diagram can reveal several common issues affecting the midfoot:
-
Plantar Fasciitis: One of the most common causes of heel and arch pain, plantar fasciitis involves inflammation of the plantar fascia—a thick band of tissue running along the bottom of the foot. A foot pain diagram will typically show pain radiating from the heel into the arch, especially during the first steps of the day.
-
Flat Feet: People with flat feet often experience pain in the arch and midfoot region. This condition can lead to overpronation, where the foot rolls inward excessively, causing strain. A foot pain diagram might highlight pain across the entire bottom of the foot, particularly in the arch area.
-
Lisfranc Injury: This is a less common but serious injury affecting the midfoot. It occurs when the ligaments that connect the bones in this area are damaged, often due to trauma. The pain is typically localized in the top of the midfoot, which a foot pain diagram will indicate clearly.
4. Hindfoot and Ankle Injuries: Clues from the Diagram
The hindfoot, which includes the heel and ankle, is another common area for foot pain. A foot pain diagram can be particularly useful in identifying injuries here, as the location of the pain can tell a lot about the underlying issue:
-
Achilles Tendonitis: This injury involves inflammation of the Achilles tendon, which connects the calf muscles to the heel bone. Pain is usually felt at the back of the heel and lower calf, which will be clearly highlighted on a foot pain diagram.
-
Heel Spurs: These bony growths form on the bottom of the heel and can cause sharp pain, especially when standing or walking. A foot pain diagram will typically show pain right in the heel area.
-
Ankle Sprains: Ankle sprains are incredibly common, especially for athletes. A foot pain diagram will help show the severity of the sprain by indicating pain around the outer or inner sides of the ankle.
5. How a Foot Pain Diagram Helps Diagnose Injuries
When you visit a podiatrist or orthopedic specialist for foot pain, they may use a foot pain diagram as a diagnostic tool. By indicating where you’re experiencing discomfort, the specialist can narrow down potential causes of the pain. Here’s how a diagram aids in diagnosis:
-
Pinpointing Pain Location: A foot pain diagram allows patients to visually indicate where the pain is coming from. Since different injuries and conditions tend to affect specific areas of the foot, this information can help doctors make an accurate diagnosis.
-
Identifying Patterns: Foot pain diagrams can also reveal patterns in pain distribution, such as whether it is localized to one part of the foot or spreads out. For example, conditions like plantar fasciitis can cause pain that starts in the heel but radiates through the arch, a pattern easily visible on a diagram.
-
Tracking Progress: Foot pain diagrams aren’t just useful for initial diagnosis—they can also help track the progress of treatment. Patients can use updated diagrams to show whether their pain is decreasing, staying the same, or shifting to other areas.
6. Common Treatments for Foot Pain
Once the source of your foot pain is identified using a foot pain diagram, your doctor will recommend the appropriate treatment. Some common treatments include:
-
Rest and Ice: For many acute injuries, resting the foot and applying ice can help reduce pain and swelling.
-
Physical Therapy: Strengthening and stretching exercises can help address issues like plantar fasciitis, Achilles tendonitis, and flat feet.
-
Orthotics: Custom-made shoe inserts can provide support and alleviate pain caused by conditions like flat feet or high arches.
-
Medications: Anti-inflammatory medications may be prescribed to reduce pain and swelling, particularly in cases of tendonitis or arthritis.
-
Surgical Intervention: In more severe cases, such as advanced bunions or fractures, surgery may be necessary to correct the issue.
Conclusion
A foot pain diagram is an invaluable tool in understanding and diagnosing foot injuries. It helps both patients and healthcare professionals pinpoint the location and cause of the pain, allowing for more accurate and efficient treatment. By using a diagram to identify the area of discomfort, specialists can offer tailored solutions to alleviate pain and improve foot function.
For those dealing with persistent foot pain, seeking professional care is essential. If you’re in need of expert care, consider exploring Foot Pain treatment in Scottsdale, AZ, where specialists can use advanced diagnostic tools like foot pain diagrams to help get you back on your feet pain-free.